Why EE?
- The only dedicated electrical engineering diploma in Singapore with an emphasis on sustainability
- Strong focus on growth areas in electrification, decarbonisation, and digitalisation to unlock exciting opportunities in the green energy economy!
- Choose from multiple pathways to meet your unique aspiration
- Unlock new opportunities for your career and further studies with a Second Major in Business and new Cross-Disciplinary Specialisations in emerging fields
About EE
As Singapore progresses towards a sustainable future under the SG Green Plan 2030, the Diploma in Electrical Engineering (EE) equips you with the expertise to transform the energy landscape. Focusing on electrification, digitalisation, and decarbonisation, this course prepares you for the demands of a low-carbon economy. Through a future-ready curriculum, you’ll gain the skills to drive sustainable energy solutions and contribute to Singapore’s green transition.
Build a strong foundation in designing and operating electrical systems, from sustainable technologies like solar energy and energy storage to the electrification of homes, transport, and industries. You will also explore the digital transformation of the energy sector, leveraging smart grids, data analytics, and AI to optimise energy use and enhance system efficiency.
Engage in real-world learning through the EE curriculum, where you will get to work with leading industry players such as Beckhoff Automation, National Instruments, Delta Electronics and Yinson GreenTech.
Start your uni studies ahead of your peers through the NP-NUS Pathway*! This programme allows you to read uni modules and earn credits that count towards your future degree at NUS.
*Offered from AY 2026/2027
You can personalise your learning journey with these pathways:
- Smart Energy System Specialisation
Drive digital transformation of the energy sector through advanced sensors, IoT devices, and AI to implement smart energy management. - Sustainable Power Engineering Specialisation
Dive into electrical distribution and utility systems while exploring sustainable energy technologies. Explore clean energy solutions such as solar photovoltaic systems, and develop the skills to design, integrate, and manage these systems effectively. - Cross-Disciplinary
Get future-ready by acquiring transferable skills in niche engineering fields by specialising in AI for Engineers, Operational Technology Cybersecurity or Space Technology. - Elective Modules Option
Select four electives to explore emerging technological trends and concepts. This option enhances your career resilience and keeps you competitive as Singapore’s energy landscape evolves. - Capstone Project Option
Apply your knowledge to tackle real-world challenges while deepening your technical expertise. - Industry Immersion Pathway
Gain real-world experience, expand your professional network, and build skills for your future with the Industry Immersion Pathway, which offers a choice between a one-year internship or project. - Double Major*
Get an extra edge by pursuing a Second Major in Business. This dual qualification will unlock new opportunities for your career and further studies.
*For selected students only
Overview of Your EE Journey
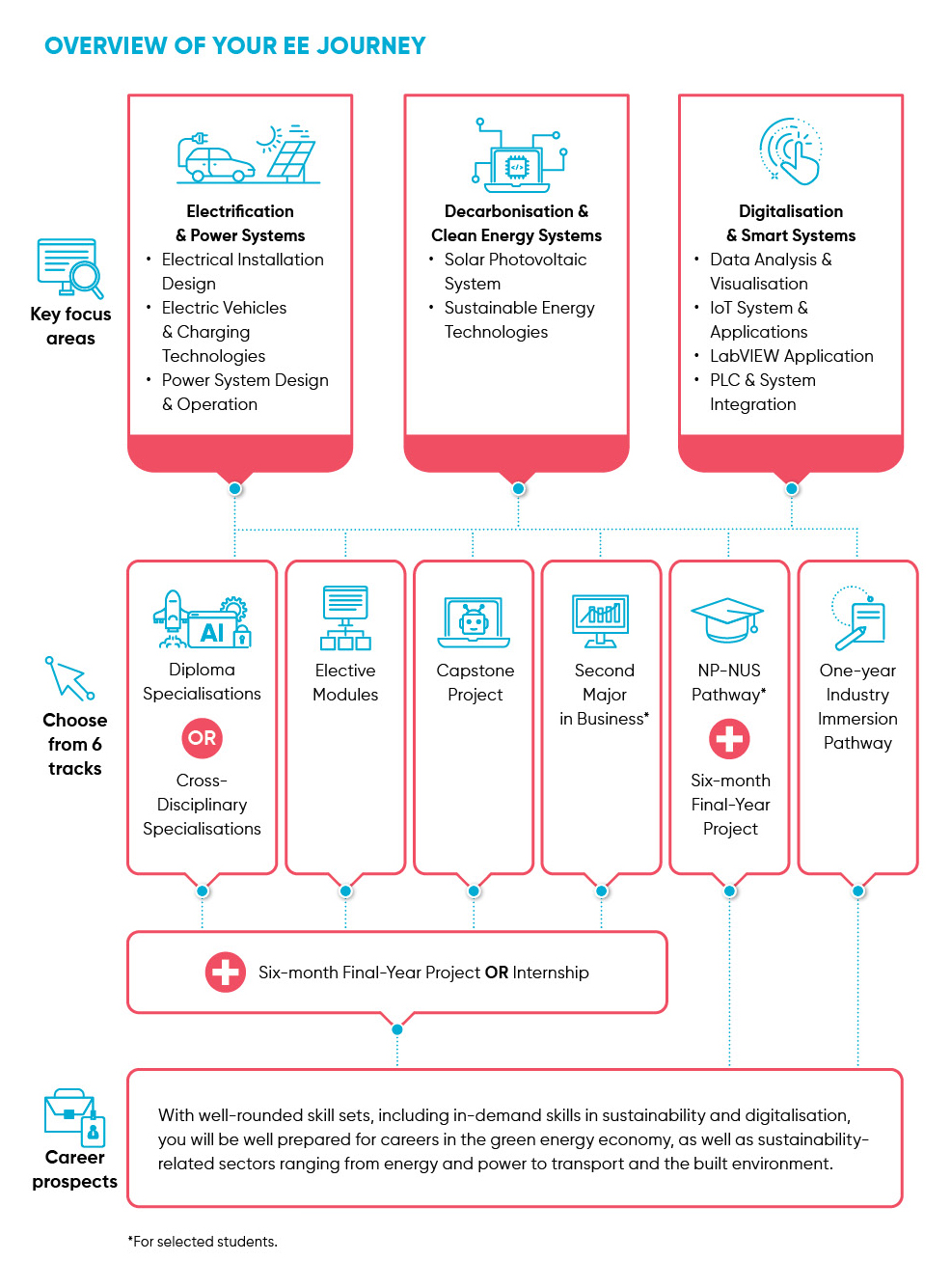
Highlights
The Future is Green
Thanks to our collaboration with Yinson
GreenTech, you can explore real-world
engineering solutions through our new
green energy infrastructure. Comprising the
IoT-enabled smart energy management
technology centre synergy.lab, a solar
farm, and on-site EV charging facilities,
this purpose-built living lab is designed
to prepare you for exciting careers in the
renewable energy field.
With our new on-campus green energy infrastructure, there’s no better place to acquire the skills to seize opportunities in the growing renewable energy field! Experiment with sustainable energy solutions at synergy.lab – and gain hands-on experience in managing a solar farm and EV charging infrastructure.
Watch this video to find more about the synergy.lab.
Joint Collaboration Final-Year Project
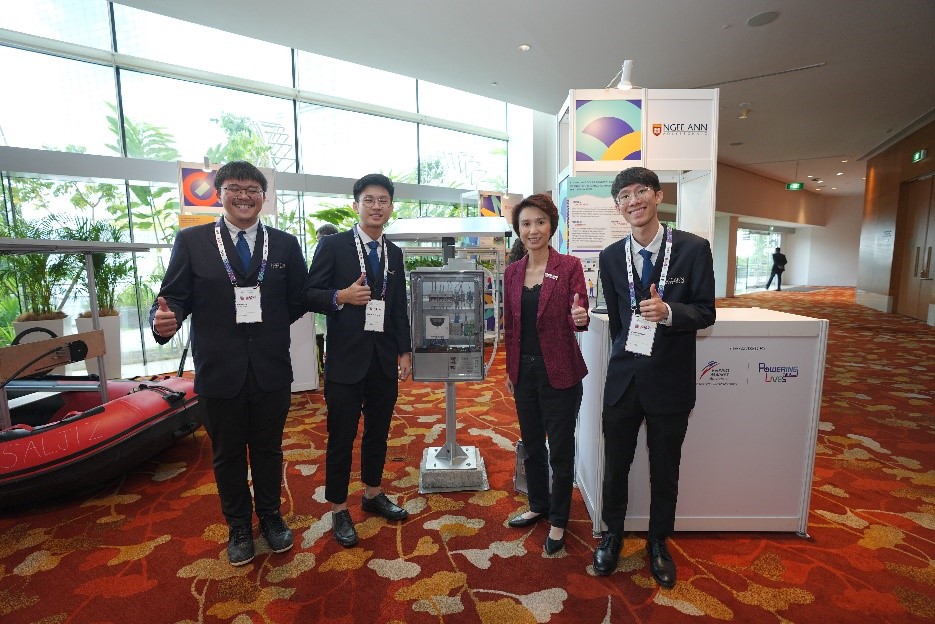

Final-year student Ryan Soh worked with Solar Energy Research Institute of Singapore (SERIS) at NUS for his final-year-project. He designed and built a test bedding system to monitor and assess the performance of different types of solar photovoltaic
modules. The project was showcased at the Singapore International Energy Week 2022, where Ryan got to present it to Ms Low Yen Ling, Minister of State for Culture, Community & Youth and Trade & Industry.
Further Studies
This diploma is recognised by leading universities both
locally and abroad. You may be granted advanced
standing or module exemptions when applying for
related degree programmes at local universities and
overseas universities in countries such as Australia and
the United Kingdom.
Graduates can further upgrade their skills through the Specialist Diploma in Solar Photovoltaic Engineering and Monitoring offered by NP.
Careers
With the Singapore Green Plan 2030, electrical engineers
are increasingly in demand across sustainability-related sectors such as energy and power, the built
environment, and transport. With a Second Major in
Business, you will be equipped to take on expanded
career roles, such as engineering project financing.
You can look forward to pursuing rewarding careers in
these job roles:
- Assistant Engineer in
- Power
- Project Development
- Commissioning
- Operation and Maintenance
- Solar PV Project Development Supervisor
- Technical Officer (Power Distribution Systems, Engineering & Maintenance, Solar PV & Energy Storage Systems)
- Energy Retail Executive
- Project Financing Executive
Entry Requirements
AGGREGATE TYPE ELR2B2-C
To be eligible for consideration, candidates must have the following GCE ‘O’ Level examination (or equivalent) results.
| Subject | 'O' Level Grade |
|---|---|
| English Language | 1-7 |
| Additional Mathematics/Mathematics | 1-6 |
| Any one of the following subjects: Biology Biotechnology Chemistry Computing/Computer Studies Design & Technology Electronics/Fundamentals of Electronics Physics Science (Chemistry , Biology) Science (Physics, Biology) Science (Physics, Chemistry) | 1-6 |
Applicants must also fulfil the aggregate computation requirements for the ELR2B2-C Aggregate Type ( English Language, 2 relevant subjects and 2 other best subjects) listed at www.np.edu.sg/docs/ELR2B2.pdf.
For students with other qualifications, please refer to the NP website for the entry requirements and admissions exercise period.
Candidates with colour vision deficiency, severe vision deficiency, profound hearing deficiency, uncontrolled epilepsy and/or severe physical impairments may encounter difficulties meeting the course requirements and expectations.
What You Will Learn
Engineering Mathematics 1
This module is designed to provide students with the fundamental skills in mathematics required to solve basic engineering problems. Topics are introduced in an order that is intended to keep abreast of the application requirements in engineering modules. The emphasis in each topic is on simple applications and problem solving. Topics include algebra, trigonometry, logarithms, plane analytic geometry, matrices and complex numbers. Throughout the module, there is appropriate use of a Computer Algebra System.
Electrical Engineering Fundamentals
This module provides a foundation in electricity covering basic concepts of electrical circuits and the methods used to analyse them. The module emphasises the understanding of the basic electrical circuit laws (Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Voltage and Current Laws) and network theorems, and their application to electrical network analysis. Topics covered include fundamentals of electricity, network theorems, capacitance, electromagnetic induction and inductance, AC waveform and transformer fundamentals.
Mechanical Engineering Fundamentals
This module introduces students to the study of external forces in two dimensions and their effect on particles and rigid bodies that are at rest and at simple linear motion. Students learn the knowledge and skills to analyse the forces acting on the bodies by drawing free-body diagrams and applying the conditions of equilibrium. This module also aims to equip students with the skills to analyse problems of rigid bodies in two dimensions linear motion. Topics include forces and resultants, moments and couples, equilibrium, plane friction, kinematics and kinetics of linear motion.
Programming
This practice-oriented module equips students with basic knowledge and skills in computer programming using a suitable high-level language. The main topics include basic computer programming concepts and fundamental programming constructs such as sequences, selection and repetition.
Career & Engineering Professional Preparation
This module aims to give students a head-start in their professional careers as they transit into a polytechnic engineering education. The module will equip students with knowledge and skills that can help them chart, navigate and advance in their individual education and career pathways. Students will be guided in adopting a design thinking approach towards making their education and career plans. They will be exposed to career-centric self-assessment tools and online resources. As part of our efforts to help students benefit from the ubiquity of a professional online presence, students will also establish their online professional brand by showcasing their marketable knowledge, skills and competencies.
To kickstart our students personal and professional development, the module will also impart various knowledge and skills, such as, cultural intelligence, financial literacy, digital literacy, industry networking and safety. The topic on safety will be taught according to the Competency Unit “Develop a Risk Management Implementation Plan” from the Singapore Workforce Skills Qualifications (WSQ) National Competency Standard. To augment this qualification, students will participate in industry engagements and service projects to glean the importance of safety in the engineering profession and societal context.
Innovation Made Possible^
This module aims to help students discover and hone their innate ability to think creatively and come up with innovations to tackle problems close to their hearts. Underpinned by the Design Thinking framework, students will be sensitised to the process of user-centric problem solving. They will be introduced to concepts such as empathy, problem-definition, ideation, prototyping and testing through a practical approach featuring engaging out-of-classroom activities, just-in-time masterclasses and a hands-on, “learning by doing” delivery format. Ultimately, the module will help students recognise that innovation is attainable and fun and develop creative confidence to explore new ideas in their studies and beyond.
English Language Express^*
^* For selected students only
^Critical Core modules account for 13 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in communication, innovation
and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary
project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile
and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
Engineering Mathematics 2
This module is designed to provide students with the fundamental skills in mathematics required to solve basic engineering problems. Topics are introduced in an order that is intended to keep abreast of the application requirements in engineering modules. The emphasis in each topic is on simple applications and problem solving. Throughout the module, there is appropriate use of a Computer Algebra System. Topics include trigonometry, differentiation and simple integration with applications.
This module equips students with foundational knowledge of electric circuit analysis, focusing on alternating current (AC) systems. Key DC network theorems are extended to AC circuits, where impedance due to capacitance and inductance is introduced. Students will learn to analyse AC circuits in series, parallel, and series-parallel configurations, gaining a solid understanding of AC power and the role of power factor. The module emphasises the importance of power factor correction in improving energy efficiency and minimising electrical losses. Students will be able to apply theoretical concepts to practical AC circuit analysis and understand their relevance in real-world electrical systems.
Analogue Electronics
The aim of this module is to lay the foundations in analogue electronics. At the end of this module, students will acquire content knowledge and understanding on the basic concepts of analogue electronics and some applications. Key topics covered in this module include operating characteristics, working principles and applications of discrete electronic devices such as various types of diodes, MOSFETs and BJTs. Practical circuits will be used to enhance and strengthen the learners’ knowledge so that they will acquire the relevant competencies to move on to more specialised modules.
Digital Fundamentals
This module introduces the basic principles of digital systems. It covers the basics of combinational and sequential logic circuits. Flip-flops and their application in counters and registers will also be discussed. This basic knowledge is essential for students to be able to analyse, troubleshoot and design basic digital circuit system.
Engineering Practical Skills New
This module provides hands-on experience in practical engineering skills, particularly in wiring and circuit assembly. Students will learn to read and interpret circuit diagrams, gaining expertise in selecting appropriate components and tools. Emphasis will be placed on building and troubleshooting electrical circuits. Safety protocols and industry-standard practices will be covered to ensure proper handling of electrical components. These skills will prepare students for more advanced electrical engineering topics and real-world applications.
Health and Wellness^
This module provides you with an opportunity to be active, keep fit and stay healthy through basic sports skill acquisition. It also aims to enhance your social and psychological well-being through a variety of sports electives while taking you through the process of character development, choice and decision making.
Confident Communication: Find Your Voice (VOICE)^
This module is designed to empower students to become thoughtful and confident communicators, while discovering their personal voice in self-expression. It equips students with the skills to communicate with impact in a variety of settings, by tailoring their message to suit audience, purpose and context. Students will learn how to utilize storytelling structures and techniques, persuasive strategies and effective visuals to connect meaningfully with their audience. The module also features a personalized growth plan that enables students to customize their learning experience according to their individual needs and aspirations. Peer learning and coaching circles provide students the platform to practise their critical reasoning and presentation skills in a safe environment. Ultimately, the module encourages students to reflect on their communication habits and develop practical strategies to enhance their effectiveness as communicators.
^Critical Core modules account for 13 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in communication, innovation and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
Electrical Machines
This module covers the basic concepts and working principles behind common types of electrical machines such as motors, transformers and generators. The module also covers industrial applications of electrical machines and introduces the importance and various concepts of maintenance.
This module covers the analytical methods and techniques for analysing electrical systems, in particular three-phase electrical systems. Through the module, students will develop confidence to analyse and solve engineering problems in electrical systems.
Microcontroller & System
This module equips students with knowledge and practical skills to design and build microcontroller-based applications. The module covers the fundamental concepts of microcontrollers and the interfacing with external applications.
PLC & System Integration
This module equips learners with the knowledge and skills to implement PLC-based control system. Leveraging on the interoperability of PLC-based systems, the module will also cover key concepts and skills of system integration required to create sustainable engineering systems.
Computer-Aided Design
This module equips students with the knowledge and skills to read and create technical drawings as a form of engineering communication. Design software from Autodesk will be used to cover different aspects of technical drawings in the field of electrical engineering.
World Issues: A Singapore Perspective^
This module takes a global approach to significant current and historical events. The aim is to enhance students' understanding of such events and issues in the context of Singapore, as well as challenge students to think critically about choices and decision-making vis-à-vis the nation state.
^Critical Core modules account for 13 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in communication, innovation and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
This module equips students with practical skills to design electrical systems for residential, commercial and industrial installations according to statutory requirements. It covers estimation of load requirements and selection of protection devices, cables and circuit protective conductors.
Power Systems Design & Operation
This module covers the technical skills and knowledge to perform basic design, testing, operation and maintenance of electrical power systems including grid and solar PV systems. The module also introduces the sound engineering practices and the relevant regulations and code of practices.
Engineering & Sustainability
This module introduces students to contemporary design thinking focused on preserving the natural environment through sustainable practices. It emphasises resource efficiency, the use of eco-friendly materials, and innovative products and processes such as lean operations, remanufacturing, and responsible sourcing. A central focus is on addressing climate change, with students learning about carbon footprints, carbon emission calculations, and decarbonisation efforts. The module highlights the local and global engineering industry's approaches to sustainability.
Power Electronics
This module provides students with a broad-based understanding of power semiconductor devices and their applications in power conversion circuits. The module also covers basic principles of control and conversion of electrical power for industrial applications and introduces motor drive systems such as variable speed drives.
Data Analysis & Visualisation
This module introduces the foundational concepts of data analysis and visualisation. Students will learn to organise and analyse datasets using software tools. Key topics include summary statistics and basic exploratory data analysis techniques. The module emphasises creating effective visual representations of data, such as charts and graphs, to communicate insights clearly. By the end of the module, students will be able to interpret and present data findings, preparing them for more advanced analytical work.
LabVIEW Applications
This module focuses on the concepts and skills of system integration required to create sustainable engineering systems. The teaching and learning will be anchored on the leading-edge engineering systems design and development platform called LabVIEW which is used by well-established industry players such as Dyson.
Smart Energy System Specialisation modules
Energy Management & Studies
This module covers the working principles and energy management of common electrical and mechanical systems. Students will learn how to define energy conservation measures and assess the economic benefits
of such measures. Energy audit process and measurement techniques will also be covered. Students will also learn to use energy measuring equipment and building modelling and simulation software tools to conduct an energy audit.
IoT System & Applications
This module brings together IoT and cloud applications to cover the concepts and skills required to monitor and manage distributed electrical systems. Applications of artificial intelligence concept
for sustainable energy systems will also be covered in the module.
Solar Photovoltaic System
This module focuses on the design, maintenance, and protection of solar PV systems. It covers key aspects of system design, including protection requirements, system sizing and inverter selection,
ensuring optimal integration with the electrical grid. Students will also learn industry maintenance practices to enhance system reliability and ensure safe operation.
Smart Grid Technologies
This module introduces students to smart grid technologies that are revolutionising the energy landscape towards a more sustainable, decentralised, and digitalised model. Students will learn the basic concepts
of distributed generation, demand management, and energy storage, which are integral to smart grid systems. The module explores how smart grids enable greater consumer interaction and real-time monitoring, enhancing the efficiency and reliability
of electricity distribution. Key topics will include renewable energy integration and intelligent energy management.
Sustainable Power Engineering Specialisation modules
Solar Photovoltaic System
This module focuses on the design, maintenance, and protection of solar PV systems. It covers key aspects of system design, including protection requirements, system sizing and inverter selection,
ensuring optimal integration with the electrical grid. Students will also learn industry maintenance practices to enhance system reliability and ensure safe operation.
Sustainable Energy Technologies
This module explores the fundamental and operational characteristics of sustainable energy technologies. Key topics include the principles of operation for renewable energy sources as well as
the associated energy conversion processes. Students will examine how these technologies harness natural resources to generate clean energy, along with their environmental and economic impacts. Students will also gain insight into the integration
of sustainable energy systems into modern infrastructure and the future potential and challenges of sustainable energy solutions.
System Modelling & Control
The module focuses on modelling dynamics and servo systems,
analysis of system responses and shaping the dynamic response through closed-loop control. Students will learn the principles of systems modelling, simulation, analysis and control, and the application of these principles in systems analysis and synthesis.
Major topics include modelling single discipline and mixed systems, Laplace transform, s-plane, standard forms, time-domain specifications, effects of control actions on system performance, and frequency response analysis.
Electric Vehicle & Charging Technologies
This module provides an in-depth overview of the key features and components of electric vehicles (EVs), with a focus on their design, operation, and performance. It introduces both current and emerging EV charging technologies, examining the various
types of charging infrastructure, from home chargers to fast-charging stations. The module also explores the integration of these charging systems into the electrical grid, highlighting their potential impact on energy demand and grid stability. Special
emphasis is placed on Singapore's transition towards sustainable mobility, addressing the challenges and opportunities of widespread EV adoption.
Year-Long Internship I
The Year-Long internship aims to enhance existing internships to enable a more structured applied-learning pathway co-supervised by company supervisors and polytechnic lecturers. Learning resources such as
learning guides would be purposefully designed to scaffold students’ learning throughout the year-long internship phase. The learning resources would cover the essential knowledge and comprise an inventory of essential on-the-job tasks designed
to cover all desired applied learning outcomes as part of the internship assessment. The contents of the learning resources will be jointly developed with the industry. Assessment would be conducted jointly by the school and company supervisors.
Final Year Project I
This year-long project module is designed to provide students with practical, hands-on experience while developing skills and knowledge comparable to those gained through traditional structured
modules. The module focuses on a comprehensive, real-world engineering problem or innovation challenge, which students will work on from inception to completion in that semester.
Throughout the project, students will engage in research,
design, analysis, prototyping, testing, and reporting, mimicking the processes found in engineering disciplines. They will be required to apply theoretical knowledge from core subjects, solve complex problems. The project will encourage collaboration,
critical thinking, and innovative problem-solving, simulating industry practices and preparing students for professional engineering roles.
AI for Engineers Specialisation Modules
Fundamentals of Machine Learning
This module introduces students to the fundamentals of machine learning principles and practices. It covers a range of machine learning models and algorithmic machine learning methods in supervised
and unsupervised learning.
Fundamentals of Neural Networks and Deep Learning
This module introduces students to the fundamental principles of neural networks and deep learning. It covers the concepts and architecture of feedforward neural networks, convolutional
neural networks, and other deep learning structures. Students will develop deep learning-based solutions to practical problems such as those in the areas of computer vision, forecasting.
Integrated Projects in Machine Learning
This module aims to integrate the knowledge learnt in the semester and apply it in practical applications. Students will work in teams and undertake the projects/case studies to develop deeper
skills in data engineering, and building up end-to-end machine learning solutions.
Operational Technology Cybersecurity Specialisation Modules
Industrial Automation
This module aims to equip students with the basic knowledge of automation technologies and their applications in the manufacturing and process industries. With the rise of new digital industrial technology,
known as Industry 4.0, students will also be introduced to smart sensors and actuators using IO-Link technology. This technology enables communication within the system (host controller) down to the sensor level.
Major topics include electro-pneumatics technology, programmable logic control and IO-Link technology. The essential hardware components used in automated systems, such as sensors, valves and actuators will be applied to the automated systems. Widely accepted industrial control programming language ladder and inline structured text will be covered, in conjunction with the learning of programming logic controllers and computer interfaces.
Laboratory work involves hands-on circuit construction and implementation using these various technologies and techniques, which enhances students’ understanding of the practical aspects of circuit designs.
Operational Technology Security
With Industry 4.0, the modern Industrial Control System (ICS) are facing more advanced threats from the Internet outside as a result of the Informational Technology/ Operational Technology (IT/OT)
convergence. Protecting them through Operational Technology (OT) cyber defense is an evolving field required to continually adapt cybersecurity strategies so as to maintain the safety and reliability of production operation.
This module aims to equip students with the knowledge of design, maintenance and protection functions within the Operational Technology (OT) environment. Using a case study of a simulated environment with Industrial Internet of Things Capability (IIoT) capability, the student perform activities with relevance to OT cybersecurity administration and maintenance in order to establish a secure OT environment. This includes performing asset discovery, managing vulnerabilities in existing OT systems, as well as performing access control management across OT systems and devices
In addition, the module also introduces the concept of industrial networking and various cyber security standards, protocols and frameworks and are knowledgeable in using various cybersecurity tools to perform their job accordingly.
Cyber Governance, Risk & Compliance
This module examines the relevant frameworks to ensure that information assets are protected within an organization. It includes the processes and policies for administering and managing a
company’s IT systems that follow the compliance framework. Concepts on risk management process, risk analysis and mitigation will also be introduced. Students will learn to evaluate risks against the company’s critical assets and deploy
safeguards to mitigate them. Control frameworks such as PCI (Payment Card Industry), ISO 17799/27002, and COBIT will be covered.
Space Technology Specialisation Modules
Satellite Systems Design and Engineering
This module provides a specialised study of satellite engineering and space systems design. Students will gain a deep understanding of orbital mechanics, the space environment, and the subsystems
essential to satellite operation, including power, thermal control, communications, and attitude determination and control. Beyond spacecraft design, the module examines the environments in which satellites are built and launched, addressing ground
infrastructure, cleanroom and testing facilities, launch vehicles, and the regulatory frameworks that govern access to space. Emphasis is placed on applying systems engineering methods to mission analysis and design, preparing students for advanced
research or professional practice in the global space industry.
Capstone Project: CanSatellite
This capstone module provides students with a unique opportunity to engage in the end-to-end development of a CanSatellite, a miniature satellite housed within the volume and shape of a soda can. Designed
to closely mimic the development, integration, testing, and validation phases of an actual satellite bus system, the project simulates industry-standard practices.
Working in multidisciplinary teams, students will design, fabricate, test, and qualify a fully functional CanSatellite that meets specified mission requirements. The experience includes iterative reviews and real-world constraints, culminating in a flight test and post-mission analysis. Emphasis is placed on systems engineering, cross-functional collaboration, and engineering documentation.
^Critical Core modules account for 13 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in communication, innovation and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
In this module, students will be attached to sponsoring companies or institutions for a period of approximately six months. During their internships, they will undertake projects assigned by the company / institution. Activities may be related to operations, research, project, maintenance, etc.
Final Year Project
In this module, students will work together in teams to design and implement a project that demonstrates their engineering skills as well as teamwork. The module is structured to encourage creativity and innovative thinking. This will also help students develop a positive work attitude and good team spirit. Students are required to demonstrate their ability and resourcefulness in implementing their selected project design solution.
Year-Long Internship II
The Year-Long internship aims to enhance existing internships to enable a more structured applied-learning pathway co-supervised by company supervisors and polytechnic lecturers. Learning resources such as learning guides would be purposefully designed to scaffold students’ learning throughout the year-long internship phase. The learning resources would cover the essential knowledge and comprise an inventory of essential on-the-job tasks designed to cover all desired applied learning outcomes as part of the internship assessment. The contents of the learning resources will be jointly developed with the industry. Assessment would be conducted jointly by the school and company supervisors.
Final Year Project II
This year-long project module is designed to provide students with practical, hands-on experience while developing skills and knowledge comparable to those gained through traditional structured modules. The module focuses on a comprehensive, real-world engineering problem or innovation challenge, which students will work on from inception to completion in that semester.
Throughout the project, students will engage in research, design, analysis, prototyping, testing, and reporting, mimicking the processes found in engineering disciplines. They will be required to apply theoretical knowledge from core subjects, solve complex problems. The project will encourage collaboration, critical thinking, and innovative problem-solving, simulating industry practices and preparing students for professional engineering roles.
Second Major in Business
Electrical Machines
This module covers the basic concepts and working principles behind common types of electrical machines such as motors, transformers and generators. The module also covers industrial applications of electrical
machines and introduces the importance and various concepts of maintenance.
Electric Circuit Analysis
This module covers the analytical methods and techniques for analysing electrical systems, in particular three-phase electrical systems.
Through the module, students will develop confidence to analyse and solve engineering problems in electrical systems.
Microcontroller & System
This module equips students with knowledge and practical skills to design and build
microcontroller-based applications. The module covers the fundamental concepts of microcontrollers and the interfacing with external applications.
PLC & System Integration
This module equips learners with the knowledge and skills to
implement PLC-based control system. Leveraging on the interoperability of PLC-based systems, the module will also cover key concepts and skills of system integration required to create sustainable engineering systems.
Finance & Accounting
for Business
The module imparts basic accounting and finance knowledge to students, in areas such as accounting equations, accounting principles, financial statements, ratio analysis, cash budgeting, short-term financing strategies, time value
of money and capital investment analysis. Students will demonstrate their understanding by using financial software to interpret financial accounting information for decision-making in business environments when working on integrated project scenarios.
Economics
This module provides students with an understanding of the core principles of microeconomics and macroeconomics with an application of these concepts in real-world business scenarios. Topics include Demand and Supply, Price
Elasticity, Market Structure, Gross Domestic Product, Unemployment, Inflation, Fiscal and Monetary policy.
World Issues: A Singapore Perspective^
This module takes a global approach to significant current and historical events.
The aim is to enhance students' understanding of such events and issues in the context of Singapore, as well as challenge students to think critically about choices and decision-making vis-à-vis the nation state.
^Critical Core modules account for 13 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in communication, innovation
and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary
project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile
and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
This module equips students with practical skills to design electrical systems for residential, commercial and industrial installations according to statutory requirements. It covers estimation of load requirements and selection of protection devices, cables and circuit protective conductors.
Power Systems Design & Operation
This module covers the technical skills and knowledge to perform basic design, testing, operation and maintenance of electrical power systems including grid and solar PV systems. The module also introduces the sound engineering practices and the relevant regulations and code of practices.
Engineering & Sustainability
This module introduces students to contemporary design thinking focused on preserving the natural environment through sustainable practices. It emphasises resource efficiency, the use of eco-friendly materials, and innovative products and processes such as lean operations, remanufacturing, and responsible sourcing. A central focus is on addressing climate change, with students learning about carbon footprints, carbon emission calculations, and decarbonisation efforts. The module highlights the local and global engineering industry's approaches to sustainability.
Power Electronics
This module provides students with a broad-based understanding of power semiconductor devices and their applications in power conversion circuits. The module also covers basic principles of control and conversion of electrical power for industrial applications and introduces motor drive systems such as variable speed drives.
Marketing
The module provides students with a strong foundation in marketing, equipping them with the skills necessary to develop effective marketing plans and strategies for the digital landscape. Students will gain a comprehensive understanding
of fundamental marketing concepts, with a specific focus on their application in the digital realm.
This module provides students with fundamental knowledge of how the external business environment, consisting of country and industry level factors, affects the overall strategy, organisational structure and various internal functions of international businesses. Students will also discuss how contemporary world affairs, such as the impact of globalisation, terrorism, pandemics, emergence of economic powers in Asia and digitalisation present both opportunities and challenges to international businesses.
Foundations of Law
This module gives an overview of the foundational principles of law within the Singapore legal system. It covers essential aspects of Criminal Law, Tort Law, Contract Law, Agency Law, Corporate Law, Intellectual
Property Law, and Technology Law. Students will gain foundational legal knowledge necessary to understand and apply legal principles in technology-related projects.
Corporate Finance
This module aims to equip students with the fundamentals of Corporate Finance. Students will acquire knowledge on the workings of a firm such as capital budgeting, equity financing and project valuation, which
encompass the use of financial management principles and valuation techniques. Board matters; ESG and corporate actions taken by a firm will also be covered.
Develop a
Business
This module is designed to let students learn how to create and validate business ideas, and subsequently start and grow a business/ venture. Students will learn how to apply the Blue Ocean Strategy to create value. Students will
also learn to analyse and present their idea using the Business Model Canvas and carry out experiential activities based on their proposed business ideas.
People & Culture
This module empowers students to design
inclusive cultures through the interdisciplinary blending of organisational psychology and human capital management principles. Students will adopt an applied approach through collaborative experiential opportunities with industry to enhance existing
human capital practices, allowing positive employee experiences and well-being to thrive.
Integrated Marketing Communications
This module aims to equip students to understand how digitalisation and AI have revolutionised the marketing communication process. Students will learn and apply marketing communication concepts, leveraging AI tools to reach and engage
the target audience at appropriate customer lifecycle touchpoints, culminating in campaign ideation and proposal pitch to a business partner.




