Why ME?
- A broad-based curriculum that prepares you for wide range of exciting careers in precision engineering, public transport, energy and chemicals, engineering services and more
- Ride the Industry 4.0 wave with in-demand digital skills like advanced modelling, industrial automation & robotics and predictive maintenance & analytics
- New sustainability focus to prepare you to help companies optimise decarbonisation efforts
- Explore a Cross-Disciplinary Specialisation New or deepen your learning by specialising in Automation Design Engineering or Mobility Design Engineering
About ME
Mechanical engineering touches virtually every aspect
of modern life. Imagine an autonomous car powered by
renewable energy and a robotic exoskeleton that can
help seniors improve their range of motion. With the
Diploma in Mechanical Engineering (ME) to give you a
head start into building such sleek technology, you’ll be
well positioned to excel in diverse fields from precision
engineering, environment and energy, facilities and
infrastructure, to the transportation sectors.
In your first year, you will learn the fundamentals of mechanical engineering with a focus on materials and design skills through modules such as Thermofluids, Materials & Manufacturing Technology and Mechanical Engineering Fundamentals. Then deepen your understanding with modules such as Engineering System Design and Strength of Materials in your second year.
You will also gain insights into the latest technologies that are reshaping the industry, such as Artificial Intelligence, robotics and the Internet of Things (IOT). Apply your skills by creating innovative clean energy solutions, developing new materials and processes, as well as designing and manufacturing products ranging from consumer products to medical devices.
In your final year, choose from the following options:
- Automation Design Engineering
Focused on system design and integration, this specialisation equips you with design, manufacturing, and maintenance skills for advanced manufacturing. These skills are applicable across various industries, preparing you for roles in design, assembly, production, and maintenance.
- Mobility Design Engineering
Through modules in Mechanical Drives System, Electrical Technology System, and Mobility System Design & Integration, you will develop electromechanical
mobility skills that are in high demand within the mobility technology sector.
- Cross-Disciplinary Specialisations
Get future-ready by acquiring transferable skills in niche engineering fields by specialising in AI for Engineers, Operational Technology Cybersecurity or Space Technology.
At ME, you will always be at the forefront of the
latest technologies by learning and collaborating on
industry-relevant projects with our partners such as
Akribis, HOPE Technik, Autodesk, Grundfos, Carrier,
and SMC Corporation.
You will also work on a final-year project to design
and develop a prototype with practical, real-world
applications.
To complete your learning journey, choose between
a six-month internship with leading organisations
such as ST Engineering, Micron Technology, and TÜV
SÜD PSB, or the Industry Immersion Pathway. This
pathway offers the option of a one-year internship
or a one-year project, giving you the chance to gain
deeper insights and hands-on experience to build
valuable skills and industry knowledge.
Start your uni studies ahead of your peers through the NP-NUS Pathway*! This programme allows you to read uni modules and earn credits that count towards your future degree at NUS.
*Offered from AY 2026/2027
Overview of Your ME Journey
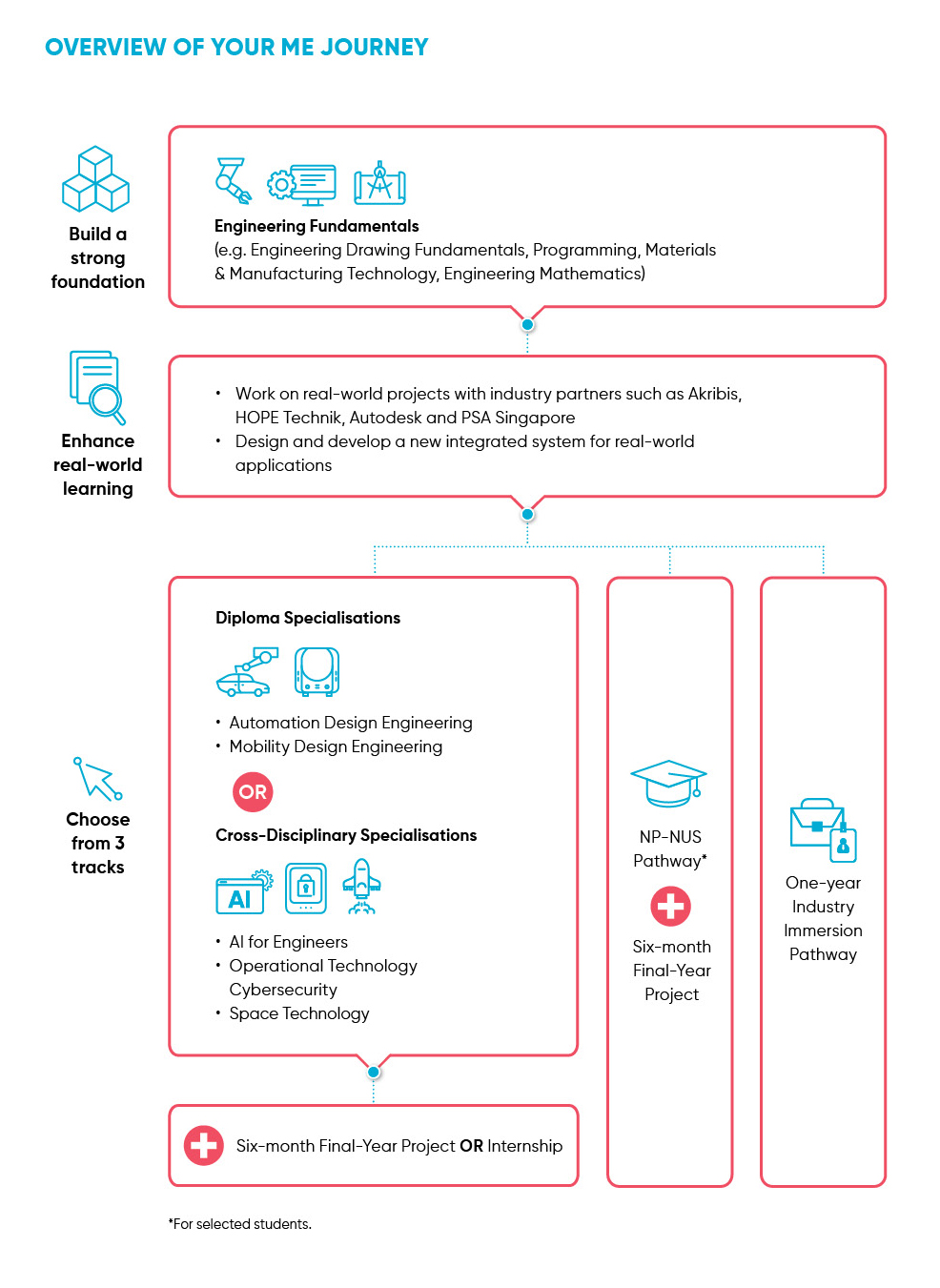
Highlights
Further Studies
You will be well prepared for further studies at both local and overseas universities. You may even be granted advanced standing in related engineering courses at:
Singapore
- Nanyang Technological University
- National University of Singapore
- Singapore Institute of Technology-University of Glasgow
Australia
- University of New South Wales
- University of Melbourne
- University of Sydney
- RMIT University
- Monash university
New Zealand
- Auckland University of Technology
- University of Auckland
United Kingdom
- University of Edinburgh
- University of Birmingham
- University of London
- Loughborough University
- Newcastle University
Careers
With a solid engineering foundation and sought-after skills, you’ll have excellent job prospects across many industries. You can look forward to pursuing roles such as:
- Assembly Engineer
- Automation Assistant Engineer
- Automotive Engineer
- Facility Engineer
- Manufacturing Engineer
- Mechanical Engineer
- Mobility Design Engineer
- Precision Engineer
- Product Engineer
- Project Engineer
- Process Engineer
- Quality Assurance Engineer
- Sales Engineer
Entry Requirements
AGGREGATE TYPE ELR2B2-C
To be eligible for consideration, candidates must have the following GCE ‘O’ Level examination (or equivalent) results.
| Subject | 'O' Level Grade |
|---|---|
| English Language | 1-7 |
| Additional Mathematics/Mathematics | 1-6 |
| Any one of the following subjects: Biology Biotechnology Chemistry Computing/Computer Studies Design & Technology Electronics/Fundamentals of Electronics Physics Science (Chemistry , Biology) Science (Physics, Biology) Science (Physics, Chemistry) | 1-6 |
Applicants must also fulfil the aggregate computation requirements for the ELR2B2-C Aggregate Type ( English Language, 2 relevant subjects and 2 other best subjects) listed at www.np.edu.sg/docs/ELR2B2.pdf.
For students with other qualifications, please refer to the NP website for the entry requirements and admissions exercise period.
Candidates with severe vision deficiency, profound hearing deficiency, uncontrolled epilepsy and/or severe physical impairments may encounter difficulties meeting the course requirements and expectations.
What You Will Learn
Mechanical Engineering Fundamentals
This module introduces students to the study of external forces in two dimensions and their effect on particles and rigid bodies that are at rest and at simple
linear motion. Students learn the knowledge and skills to analyze the forces acting on the bodies by drawing free-body diagrams and applying the conditions of equilibrium. This module also aims to equip students with the skills to analyze problems of
rigid bodies in two dimensions linear motion. Topics include forces and resultants, moments and couples, equilibrium, plane friction, kinematics and kinetics of linear motion.
Electrical Engineering Fundamentals
This module
provides a foundation in electricity covering basic concepts of electrical circuits and the methods used to analyse them. The module emphasises the understanding of the basic electrical circuit laws (Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Voltage and Current
Laws) and network theorems, and their application to electrical network analysis. Topics covered include fundamentals of electricity, network theorems, capacitance, electromagnetic induction and inductance, AC waveform and transformer fundamentals.
Engineering Mathematics 1
This module is designed to provide students with the fundamental skills in mathematics required to solve basic engineering problems. Topics are introduced in an order that is intended to keep abreast
of the application requirements in engineering modules. The emphasis in each topic is on simple applications and problem solving. Topics include algebra, trigonometry, logarithms, plane analytic geometry, matrices and complex numbers. Throughout the module,
there is appropriate use of a Computer Algebra System.
Programming
This practice-oriented module equips students with basic knowledge and skills in computer programming using a suitable high-level language. The main topics
include basic computer programming concepts and fundamental programming constructs such as sequences, selection and repetition.
Career & Engineering Professional Preparation
This module aims to give students
a head-start in their professional careers as they transit into a polytechnic engineering education. The module will equip students with knowledge and skills that can help them chart, navigate and advance in their individual education and career pathways.
Students will be guided in adopting a design thinking approach towards making their education and career plans. They will be exposed to career-centric self-assessment tools and online resources. As part of our efforts to help students benefit from the
ubiquity of a professional online presence, students will also establish their online professional brand by showcasing their marketable knowledge, skills and competencies.
To kickstart our students personal and professional development,
the module will also impart various knowledge and skills, such as, cultural intelligence, financial literacy, digital literacy, industry networking and safety. The topic on safety will be taught according to the Competency Unit “Develop a Risk Management
Implementation Plan” from the Singapore Workforce Skills Qualifications (WSQ) National Competency Standard. To augment this qualification, students will participate in industry engagements and service projects to glean the importance of safety in
the engineering profession and societal context.
Innovation Made Possible^
This module aims to help students discover and hone their innate ability to think creatively and come up with innovations to tackle problems close to
their hearts. Underpinned by the Design Thinking framework, students will be sensitised to the process of user-centric problem solving. They will be introduced to concepts such as empathy, problem-definition, ideation, prototyping and testing through
a practical approach featuring engaging out-of-classroom activities, just-in-time master-classes and a hands-on, “learning by doing” delivery format. Ultimately, the module will help students recognise that innovation is attainable and fun
and develop creative confidence to explore new ideas in their studies and beyond.
English Language Express^*
^* For selected students only.
^Critical Core modules account for 13 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in communication, innovation
and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary
project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile
and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
Materials & Manufacturing Technology
This module introduces students to properties of common engineering materials with emphasis on mechanical testing methods, heat-treatment, international standard specifications,
and selection and applications of such materials. Topics include classification of materials, mechanical testing, alloying, steels, non-ferrous alloys, plastics, ceramics and composites. For manufacturing technology, students will acquire the basic knowledge
and skills of manufacturing processes, including drilling, turning, milling, grinding, non-conventional machining, welding and assembly.
Strength of Materials
This module aims to provide students with the foundational knowledge of
strength of materials with emphasis on applications and problem solving. It introduces to students the methods in the calculation of stresses and strains in various structural members such as beams, columns and shafts. Taking into account the material
properties, students would then be able to apply the methods to predict the response of a structure under loading. Topics include simple stresses and strains, torsion in shaft, shear force and bending moment diagrams, stresses in beams, combined stresses
and experimental stress analysis.
Engineering Mathematics 2
This module is designed to provide students with the fundamental skills in mathematics required to solve basic engineering problems. Topics are introduced in an order that
is intended to keep abreast of the application requirements in engineering modules. The emphasis in each topic is on simple applications and problem solving. Throughout the module, there is appropriate use of a Computer Algebra System. Topics include
trigonometry, differentiation and simple integration with applications.
Thermofluids
Students will learn the basic laws governing the behaviour of fluids under the influence of energy transfer. Topics include systems concept,
temperature and pressure, fluid statics, fluid in motion, continuity equation, laminar and turbulent flows, ideal incompressible flow, Bernoulli’s equation, flow measurement and Pitot tube, external flow and application of thermofluid’s principles
in simple engineering systems.
Engineering Drawing Fundamentals
This module aims to enable students to understand basic engineering drawing concepts, definitions and the purpose of conveying all the information necessary for
manufacturing a product or a part. Students will also work in teams and undertake the projects/case studies underpinned by the design thinking and computer-aided design (2D skills) approach. Upon completion of the module, students will be able to apply
the skills and develop confidence in tackling projects at higher levels.
Confident Communication: Find Your Voice (VOICE)^
This module is designed to empower students to become thoughtful and confident communicators, while
discovering their personal voice in self-expression. It equips students with the skills to communicate with impact in a variety of settings, by tailoring their message to suit audience, purpose and context. Students will learn how to utilize storytelling
structures and techniques, persuasive strategies and effective visuals to connect meaningfully with their audience. The module also features a personalized growth plan that enables students to customize their learning experience according to their individual
needs and aspirations. Peer learning and coaching circles provide students the platform to practise their critical reasoning and presentation skills in a safe environment. Ultimately, the module encourages students to reflect on their communication habits
and develop practical strategies to enhance their effectiveness as communicators.
Health & Wellness^
This module provides students with an opportunity to be active, keep fit and stay healthy through basic sports skill
acquisition. It also aims to enhance student’s social and psychological well-being through a variety of sports electives while taking them through the process of character development, choice and decision making.
^Critical Core modules account for 13 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in communication, innovation
and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary
project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile
and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies
This module builds on the foundational materials and manufacturing knowledge gained in the first year, deepening students' understanding of both advanced
manufacturing technologies and material applications. The module covers key theoretical concepts and practical skills in advanced manufacturing processes, focusing on techniques prevalent in precision engineering industries and advanced materials applications.
Students will gain hands-on experience in CNC machining and programming, with practical assignments and demonstrations designed to enhance their competence. In addition, the module explores the properties, characterization, and fabrication of advanced
materials, providing students with the knowledge needed to apply these materials in engineering design. By integrating both advanced manufacturing technologies and materials science, the module prepares students to confidently work with cutting-edge processes
and materials in their future careers.
Applied Mechanics
This is a follow-on module from Mechanical Engineering Fundamentals. It will equip students with the necessary skills to analyse problems of rigid bodies at rest
and in motion. Topics include trusses, friction, work energy method, power and efficiency and impulse momentum method. This knowledge plays an important role in many diverse engineering applications in the modern world, such as the design of cars, structures,
airplanes, and various types of machines. Students will be guided to solve engineering problems using these mechanics principles
Industrial Automation
This module aims to equip students with the basic knowledge of automation technologies
and their applications in the manufacturing and process industries. With the rise of new digital industrial technology, known as Industry 4.0, students will also be introduced to smart sensors which have the ability to collect data that can be used for
data analysis.
Major topics include electro-pneumatics technology, programmable logic control and IO-Linked technology (for smart sensors). The essential hardware components used in automated systems, such as sensors, valves and actuators will
be applied to the automated systems. Widely accepted industrial control programming language ladder and inline structured text will be covered, in conjunction with the learning of programming logic controllers and computer interfaces.
Laboratory
work involves hands-on circuit construction and implementation using these various technologies and techniques, which enhances students’ understanding of the practical aspects of circuit designs.
Applied Thermofluids
Thermo-fluids
is a module of science and engineering encompassing 2 intersecting fields namely Thermodynamics and Fluid mechanics. In relation to mechanical engineering, Thermodynamics is the science of converting energy involving heat to mechanical work and Fluid
Mechanics is the study of physical forces in a system in the presence of fluid when at rest or in motion. Heat energy had to be transported by fluid in order to undergo various thermodynamic processes and becomes mechanical work eventually. The way fluid
would flow ultimately dominates the entire thermal energy conversion process.
This module extends the coverage of Thermofluids in year 1, which further the basic concepts and principles of Thermodynamics and Fluid mechanics concepts. Behaviour
of fluids under different conditions like static, dynamic and under the influence of heat will be covered in further details. The most important 2nd law of Thermodynamics will be introduced. Subsequently, Basic Engineering cycles developed from the
2nd law including Steam power cycles and Gas power cycles will be discussed. Students will also be taught on the methods of Engine performance testing.
Engineering & Sustainability
This module aims to develop in our students
the knowledge, skills and disposition towards sustainability by introducing them to the dominant environmental and climate change issues caused by technological developments. Students will learn about sustainability design in the context of engineering
design considerations, such as, resource efficiency, environmentally friendly materials, innovative sustainable products, lean and green operations, remanufacturing and responsible sourcing. In collaboration with community and industry partners,
Service-Learning projects provide opportunities for the students to apply and hone their Green skills while developing a deeper understanding of environmental sustainability issues and their social impacts both locally and globally.
The
module also encourages students to appreciate and explore green job opportunities in engineering. Career and Professional Preparation 2 is incorporated to equip students with the skills necessary to seek and secure such work opportunities. They
will also be equipped to communicate their personal brand more effectively. As students sharpen their communication skills, they will also learn how to market themselves effectively.
Mechanics of Machines & Materials
This module will provide students with the experience of solving engineering problems based on the principles and theories covered in the earlier Mechanics modules.
Topics include velocity and acceleration diagrams, effects of the mass of members of mechanism, friction mechanisms and the effects of friction on screw threads and belt drives, balancing of shafts and its application to gears and pulleys, and the causes
and control of machinery vibration.
Engineering System Design
This module aims to equip students with the fundamental knowledge and practice of the engineering design process, the applications of engineering principles and analysis in the design,
sizing and selection of components such as electric motor, coupling, gears, bearing, chain drives, and fastener. This module will also introduce the basic concept of Geometrical Dimensioning & Tolerance (GD&T) to the students. Case studies of
existing machines and systems, guided tutorials, quizzes, assignments, and a practical project will be used to reinforce the theoretical aspects.
Project Management
This module provides students with an understanding of the various
aspects of project management procedures. The module also equips students with various project management tools. The module is supplemented with tutorial assignments, and case studies are included to reinforce basic understanding and concepts which can
be applied in practical situations.
Quality Systems & Analytics
This module prepares students to apply quality system management techniques and principles in their future workplace. Topics include Quality Systems
and Audits, quality tools and techniques including the application of statistical software for process control, Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility, Hypothesis Testing, Design of Experiments, Statistical Process Control, and Mistake Proofing to optimise
and improve products and processes. Process Capability Analysis, Lean Manufacturing for waste elimination and Six Sigma initiatives for defect reduction will also be discussed.
Computer-Aided Design & Analysis
This module is
a practice-oriented module designed to give students an appreciation of the scope of computer graphics and hands-on practice on the applications of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) in engineering design. This module aims to help the students in the application
of the drafting concepts and modeling techniques for development of product models in the design process. Students will learn the principles and capabilities of CAD through three dimensional (3D) solid modeling of engineering components and assembly.
A project is used to consolidate the concepts and techniques learnt CAD module and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) module. Another project is used to consolidate the concepts and techniques learnt CAD module and ED (Engineering Design) module. Students
will also use the software to do some basic stress analysis and motion simulation.
World Issues: A Singapore Perspective^
This module takes a global approach to significant current and historical events. The aim is to
enhance students’ understanding of such events and issues in the context of Singapore, as well as challenge students to think critically about choices and decision-making vis-à-vis the nation state.
^Critical Core modules account for 13 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in communication, innovation
and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary
project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile
and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
Project ID: Connecting the Dots^
Project ID aims to prepare students for an increasingly globalised and interconnected world where problems are multi-faceted and require interdisciplinary research and collaboration to solve. Using
a project-based learning approach, students will have the opportunity to work in a multi-disciplinary team with students from across the polytechnic to investigate and propose comprehensive recommendations for a pressing real-world problem affecting
Singapore. they will be guided to step out of your disciplinary silos and effectively communicate and collaborate with peers from different backgrounds. The module seeks to develop independent learning skills and the ability to synthesise diverse
strands of knowledge to solve a complex problem, while impressing on them the importance of being a responsible global citizen.
Automation Design Engineering Specialisation Modules
Automation System Design and Integration
This module aims to integrate the knowledge learnt in the semester and apply to a real-world automation project and understand the relevance and application of the modules learnt. Students
will work in teams and undertake the project development underpinned by the design thinking Computer-Aided Design approach. On completion of the module, students will be able to apply the skills and develop confidence in tackling design projects
Design for Manufacturing & Assembly
This module covers design thinking concepts that enable our students to design and create engineering solution to real word problem. It also provides students with foundation and
knowledge to understand and apply Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) mythology to enhance their engineering design. Students will also be introduced various engineering measurement tools and mythology to ascertain their design dimensional
accuracy.
This module also introduces design of Jigs and Fixtures to enable students to design guide to enable manufacturing tools to improve production of identical and interchangeable components. Students will have the opportunity to work through
many real word-based case studies to better understand and apply these concepts and mythologies introduced in this module.
Smart Sensors & Actuators
This module aims to provide students with broad knowledge in
the working principle and application of smart engineering sensors and actuators. It provides students with the opportunities to appreciate and gain insight into the inter-connectivity and inter-dependence of smart sensors and actuators in a digital
manufacturing environment. Students will acquire design, critical-thinking and problem-solving skills through case studies and group projects.
Mobility Design Engineering Specialisation Modules
Mobility System Design and Integration
In this module, students will work as a team using computer aided design (CAD) software to design and integrate a concept vehicle. Students would be applying the knowledge they have learned
from other modules and complete a workable 3D CAD model which includes chassis and body design, steering system design, brake system design, suspension system design, powertrain design and configuration.
Mechanical Drives System
This module aims to give an overview of the mechanical systems in a modern vehicle, such as engine, transmission, steering system, suspension system and brake system. Student will deepen their knowledge in the fundamentals, functions, operations
of these systems through theoretical and hands on approach. The students can use some of the knowledge gained from this module and apply into their concept vehicle design and integration.
Electrical Technology System
This module aims to introduce powertrain and electric systems for a vehicle, including battery electric vehicle (BEV), so that it will equip the students with the knowledge and hands-on practice needed to systematically understand the both systems
and the components, energy storage and conversion. The students can use some of the knowledge gained from this module and apply into their concept vehicle design and integration.
Capstone Project
This module immerses
students in the entire project cycle, requiring them to leverage the knowledge and skills they have gained through course of studies to address real-world challenges in the industry. Students will work in groups on projects their performance will
be evaluated through continuous assessments.
Year-Long Internship I
The Year-Long internship aims to enhance existing internships to enable a more structured applied-learning pathway co-supervised by company supervisors and polytechnic lecturers. Learning resources such as
learning guides and taskbooks would be purposefully designed to scaffold students’ learning throughout the year-long internship phase. The learning guides and taskbooks would cover the essential knowledge and comprise an inventory of essential
on-the-job tasks designed to cover all desired applied learning outcomes as part of the internship assessment. The contents of the learning guides and taskbooks will be jointly developed with the industry. Students would submit a final report at the
end of each semester and present what they have learned. Assessment would be conducted jointly by the school and company supervisors.
Final Year Project I
This year-long project module is designed to provide students with practical, hands-on experience while developing skills and knowledge comparable to those gained through traditional structured modules.
The module focuses on a comprehensive, real-world engineering problem or innovation challenge, which students will work on from inception to completion in that semester.
Throughout the project, students will engage in research, design,
analysis, prototyping, testing, and reporting, mimicking the processes found in engineering disciplines. They will be required to apply theoretical knowledge from core subjects, solve complex problems. The project will encourage collaboration, critical
thinking, and innovative problem-solving, simulating industry practices and preparing students for professional engineering roles.
AI for Engineers Specialisation Modules
Fundamentals of Machine Learning
This module introduces students to the fundamentals of machine learning principles and practices. It covers a range of machine learning models and algorithmic machine learning methods in supervised
and unsupervised learning.
Fundamentals of Neural Networks and Deep Learning
This module introduces students to the fundamental principles of neural networks and deep learning. It covers the concepts and architecture of feedforward neural networks, convolutional
neural networks, and other deep learning structures. Students will develop deep learning-based solutions to practical problems such as those in the areas of computer vision, forecasting.
Integrated Projects in Machine Learning
This module aims to integrate the knowledge learnt in the semester and apply it in practical applications. Students will work in teams and undertake the projects/case studies to develop
deeper skills in data engineering, and building up end-to-end machine learning solutions.
Operational Technology Cybersecurity Specialisation Modules
Industrial Automation
This module aims to equip students with the basic knowledge of automation technologies and their applications in the manufacturing and process industries. With the rise of new digital industrial technology,
known as Industry 4.0, students will also be introduced to smart sensors and actuators using IO-Link technology. This technology enables communication within the system (host controller) down to the sensor level.
Major topics include electro-pneumatics technology, programmable logic control and IO-Link technology. The essential hardware components used in automated systems, such as sensors, valves and actuators will be applied to the automated systems. Widely accepted industrial control programming language ladder and inline structured text will be covered, in conjunction with the learning of programming logic controllers and computer interfaces.
Laboratory work involves hands-on circuit construction and implementation using these various technologies and techniques, which enhances students’ understanding of the practical aspects of circuit designs.
Operational Technology Security
With Industry 4.0, the modern Industrial Control System (ICS) are facing more advanced threats from the Internet outside as a result of the Informational Technology/ Operational Technology (IT/OT)
convergence. Protecting them through Operational Technology (OT) cyber defense is an evolving field required to continually adapt cybersecurity strategies so as to maintain the safety and reliability of production operation.
This module aims to equip students with the knowledge of design, maintenance and protection functions within the Operational Technology (OT) environment. Using a case study of a simulated environment with Industrial Internet of Things Capability (IIoT) capability, the student perform activities with relevance to OT cybersecurity administration and maintenance in order to establish a secure OT environment. This includes performing asset discovery, managing vulnerabilities in existing OT systems, as well as performing access control management across OT systems and devices
In addition, the module also introduces the concept of industrial networking and various cyber security standards, protocols and frameworks and are knowledgeable in using various cybersecurity tools to perform their job accordingly.
Cyber Governance, Risk & Compliance
This module examines the relevant frameworks to ensure that information assets are protected within an organization. It includes the processes and policies for administering and managing a company’s IT systems that follow the compliance framework.
Concepts on risk management process, risk analysis and mitigation will also be introduced. Students will learn to evaluate risks against the company’s critical assets and deploy safeguards to mitigate them. Control frameworks such as PCI (Payment
Card Industry), ISO 17799/27002, and COBIT will be covered.
Space Technology Specialisation Modules
Satellite Systems Design and Engineering
This module provides a specialised study of satellite engineering and space systems design. Students will gain a deep understanding of orbital mechanics, the space environment, and the
subsystems essential to satellite operation, including power, thermal control, communications, and attitude determination and control. Beyond spacecraft design, the module examines the environments in which satellites are built and launched, addressing
ground infrastructure, cleanroom and testing facilities, launch vehicles, and the regulatory frameworks that govern access to space. Emphasis is placed on applying systems engineering methods to mission analysis and design, preparing students for
advanced research or professional practice in the global space industry.
Capstone Project: CanSatellite
This capstone module provides students with a unique opportunity to engage in the end-to-end development of a CanSatellite, a miniature satellite housed within the volume and shape of a soda can. Designed to closely mimic the development, integration,
testing, and validation phases of an actual satellite bus system, the project simulates industry-standard practices.
Working in multidisciplinary teams, students will design, fabricate, test, and qualify a fully functional CanSatellite that meets specified mission requirements. The experience includes iterative reviews and real-world constraints, culminating in a flight test and post-mission analysis. Emphasis is placed on systems engineering, cross-functional collaboration, and engineering documentation.
^Critical Core modules account for 13 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in communication, innovation and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
6-month Internship (Local/Overseas)
The six-month internship will provide students with the opportunity to apply the knowledge acquired in the classroom to work situations, and demonstrate problem solving,
communication and interpersonal skills in a work environment. The programme enables students to hone their ability to work independently and in teams, while they take on one or more practical projects under the supervision of industry practitioners. The
objective is to develop a professional approach to work based on the relevant code of practice.
Final-Year Project
In this module, students will work in teams to design and develop a product or system related to a real-world project.
In the project, students learn to apply their knowledge and skills in creative problem solving, engineering and design, teamwork and project management. This module focuses on the identification of problem or need, research and design. Student are required
to fabricate the prototype, assemble the parts, test and refine the prototype, and prepare the refined design and a project report. Students are also required to do a final presentation to a panel of examiners.
Year-Long Internship II
The Year-Long internship aims to enhance existing internships to enable a more structured applied-learning pathway co-supervised by company supervisors and polytechnic lecturers. Learning resources such as learning guides and taskbooks would be purposefully
designed to scaffold students’ learning throughout the year-long internship phase. The learning guides and taskbooks would cover the essential knowledge and comprise an inventory of essential on-the-job tasks designed to cover all desired applied
learning outcomes as part of the internship assessment. The contents of the learning guides and taskbooks will be jointly developed with the industry. Students would submit a final report at the end of each semester and present what they have learned.
Assessment would be conducted jointly by the school and company supervisors.
Final Year Project II
This year-long project module is designed to provide students with practical, hands-on experience while developing skills and knowledge
comparable to those gained through traditional structured modules. The module focuses on a comprehensive, real-world engineering problem or innovation challenge, which students will work on from inception to completion in that semester.
Throughout
the project, students will engage in research, design, analysis, prototyping, testing, and reporting, mimicking the processes found in engineering disciplines. They will be required to apply theoretical knowledge from core subjects, solve complex problems.
The project will encourage collaboration, critical thinking, and innovative problem-solving, simulating industry practices and preparing students for professional engineering roles.





