Why DS?
- Become a highly sought-after AI talent with a solid foundation in data engineering and machine learning
- Choose from two exciting specialisation areas: Data Engineering or Generative AI
- Earn professional certifications from industry leaders such as Alteryx, Google, IBM, Nvidia and Singapore Computer Society
- Be among the first to earn a Second Major in Business and unlock new opportunities for your career and further studiesNEW
- Kickstart your degree with the NP-University Pathway and earn credits towards your degree while still in polyNEW
About DS
With every click, like, and share, data is being created and collected. There’s never been a greater demand for data science professionals to help businesses derive insights, drive traffic and boost profits. If you are passionate about data analytics and machine learning, and want to make your mark in the big data industry, the Diploma in Data Science (DS) is the course for you!
Besides benefitting from the expertise of ICT – co-founder of the Data School set up to train data practitioners for industry – you will get to collaborate with leading industry partners such as OCBC and Indorse.
Gain core skills in programming, databases, and analytics. Master data science fundamentals, key statistical concepts, and data visualisation techniques. All of these skills will set you up for success in roles like data analyst, junior data scientist, associate data engineer, or associate business analyst.
Hone programming and analytical skills essential for managing AI projects by working with leading enterprise platforms including Salesforce, Tableau, SAP, and Alteryx. These competencies will pave the way for future careers in project management and business consultancy.
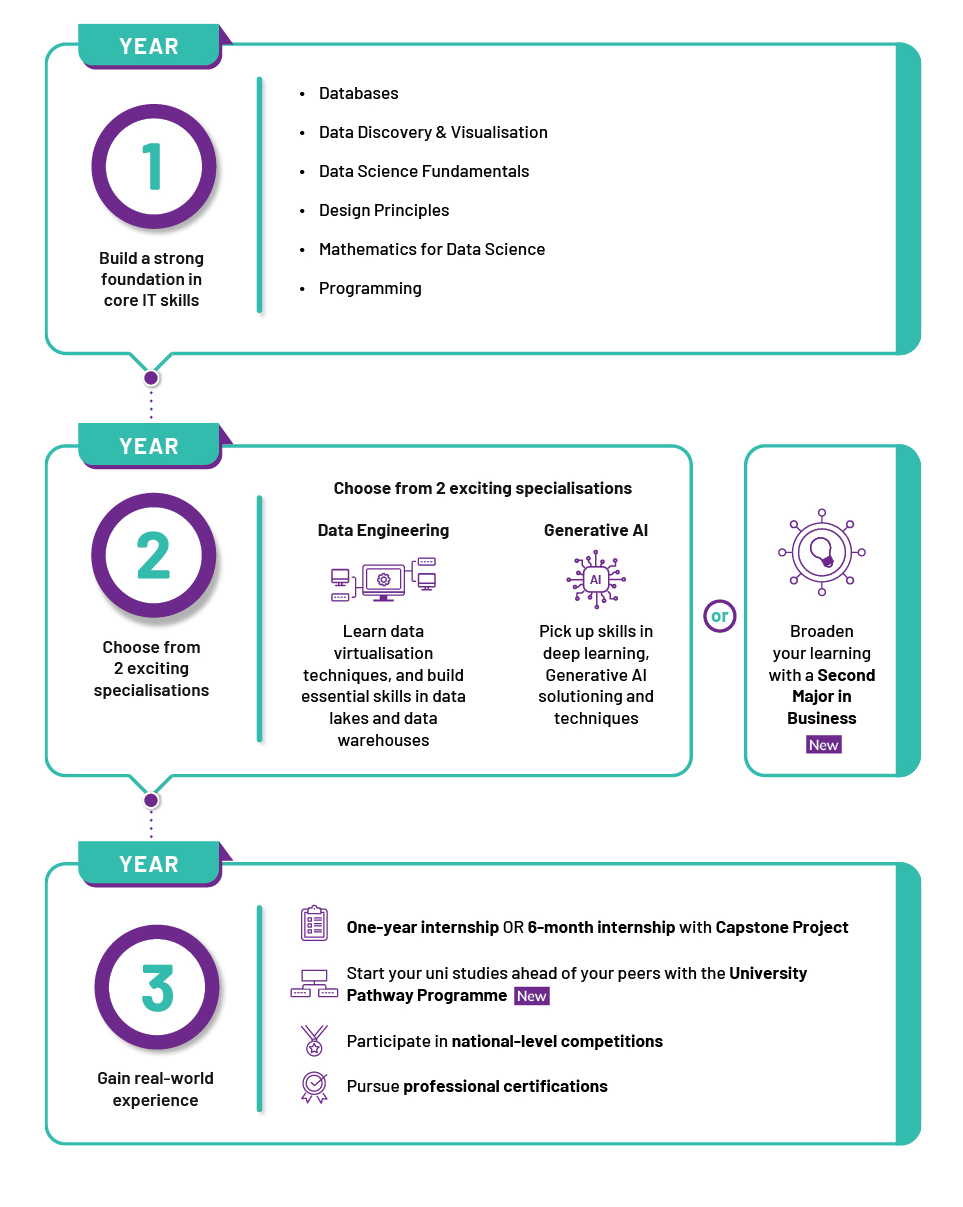
Gain an edge with one of these specialisations from your second year:
- Data Engineering
Co-developed by industry partners including Alteryx, Denodo, and Snowflake, this specialisation offers in- depth training in data pipelines, data virtualisation and data wrangling.
- Generative AI
Dive into generative AI tools and techniques, as well as deep learning. This robust curriculum will equip you for careers in this fast-evolving field.
Be among the first poly students to pursue a Second Major in Business. Gain an edge with this dual qualification, which will unlock new opportunities for your career and further studies.
Fast-track your university journey with our pathways to SMU and SUTD! These programmes let you take university modules during your diploma studies. For the SMU Pathway, you’ll gain advanced placement in their Information Systems and Computing Science programmes. Meanwhile, the Poly SUTD Scholars Programme (PSPP) allows you to explore humanities and science modules that count towards your degree at SUTD.
Boost your workplace readiness with a one-year
Industry Kickstart Programme. Engage in industry-driven data science projects, explore emerging
trends, and apply machine learning techniques in
real-world data workflows.
You will also benefit from internships, workshops,
field trips, and industry mentorship. Plus, put your
skills to the test in national-level competitions like
the PolyFintech100 Hackathon.
Gain a head start with professional certifications such as:
- Nvidia’s Certificate of Competency on Getting Started with Deep Learning
- Alteryx Core Designer
- Associate Certificate in AI Ethics & Governance by Singapore Computer Society
- Salesforce’s Lightning Experience Reports & Dashboards Specialist Superbadge
Overview of Your DS Journey
Highlights
Industry-driven Data Training
Widen your career options with the Data School, a collaboration between ICT and industry partners such as OCBC and Indorse. You can look forward to taking skills-focused short courses, which are co-designed and co-delivered with the industry to provide career-relevant training that will prepare you for future roles in data analysis and data science.

Visit https://www.cet.np.edu.sg/signature_programme/data-school/ to find out more.
Further Studies
Receive advanced standing when you apply for related degree programmes at universities both locally and abroad. These include:
- Nanyang Technological University
- National University of Singapore
- Singapore Institute of Technology
- Singapore Management University
- Singapore University of Technology and Design
You can also look forward to pursuing a specialist diploma in an analytics-related field and other advanced diploma courses at local polytechnics.
Careers
As Singapore strives to become a global hub for AI development and deployment, demand for professionals who possess skills in areas such as data extraction, wrangling, machine learning and deep learning techniques will increase. Graduates can look forward to careers in roles such as:
- Artificial Intelligence Engineer
- Associate Business Analyst
- Associate Data Engineer
- Data Analyst
- Data Engineer
Entry Requirements
AGGREGATE TYPE ELR2B2-C
To be eligible for consideration, candidates must have the following GCE ‘O’ Level examination (or equivalent) results.
| Subject | 'O' Level Grade |
|---|---|
| English Language | 1-7 |
| Additional Mathematics/Mathematics | 1-6 |
| Any one of the 2nd group of Relevant Subjects for the ELR2B2-C Aggregate Type | 1-6 |
Applicants must also fulfil the aggregate computation requirements for the ELR2B2-C Aggregate Type ( English Language, 2 relevant subjects and 2 other best subjects) listed at www.np.edu.sg/docs/ELR2B2.pdf.
For students with other qualifications, please refer to the NP website for the entry requirements and admissions exercise period.
Candidates with severe vision deficiency may encounter difficulties meeting the course requirements and expectations.
What You Will Learn
Computing Mathematics (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces the basic concepts of relations and functions, matrices and methods of statistics and their applications relevant to IT professionals. The main emphasis in this module is to develop students’ ability in solving quantitative problems in computing mathematics, probability and statistics. Topics covered include fundamentals of statistics and probability, discrete and continuous probability distributions.
Cyber Security Fundamentals (2 Credit Units)
This module provides an overview of the various domains of cyber security. It helps to develop an understanding of the importance of cyber security in today’s digital world. It aims to provide an appreciation of cyber security from an end-to-end perspective. It covers fundamental security concepts, tools and techniques in domains such as data, end-user, software, system, network, physical, organization, and digital forensics. It also helps to develop knowledge and skills in identifying common cyber threats and vulnerabilities, and to apply techniques to tackle these issues.
Data Science Fundamentals (2 Credit Units)
This module provides an overview of Data Science, its importance in the world of data and how it affects the competitiveness of organizations. Learners will learn about the different areas within Data Science and the core pillars essential to practise in the area. Students will also be introduced to Design Thinking. Indicative topics include Introduction to Data Science, Big Data and Analytical Design Thinking.
Design Principles (2 Credit Units)
This module introduces students to basic elements and principles of design. Students will practice visual communication and self-branding through aesthetic use of line, shape, form, color, texture, typography, scale, contrast, rhythm and balance. Students will be trained in the usage of digital design tools and application of modern industrial practices to communicate the concepts, designs and solutions.
Fundamentals for IT Professionals 1 (2 Credit Units)
This module provides a broad introduction to the field of ICT by exploring the roles, professional practice, ethical expectations and career development paths of IT professionals. Through a guided inculcation of interpersonal and teamwork skills with strong team bonding spirit, the module aims to deepen students’ commitment to the sector that the course prepares them for. In addition, students will be required to begin charting their career path in the ICT industry by considering crucial aspects such as personal preferences and aptitude, job roles and responsibilities, skills needed and further education.
Programming 1 (5 Credit Units)
This module introduces the fundamentals of programming and how to develop programs using appropriate problem-solving techniques in a modular style. In this practice-oriented module, students are taught how to apply problem-solving skills using a top-down structured programming methodology and given ample practice in translating solutions into computer programs, then test and debug the programs. Topics include data types, variables, expressions, statements, selection structures, loops, simple computation and algorithms, and the use of libraries. Students will also practise the use of pseudocodes, best practices of programming, debugging techniques with the help of tools, development of test cases, and suitable program documentation. In addition, they will study various areas where application software plays a prominent part in helping organisations solve problems. Student will be given ample opportunity for independent and self-directed learning.
English Language Express* (Credit Units - NA)
English Language Express aims to give you a better grounding in the English Language and to strengthen the written and oral communications skills that you will need in your academic and professional careers. You will be engaged in writing, reading, listening and speaking activities that will develop your ability to speak and write grammatically, coherently and clearly. You will also hone your reading and listening comprehension skills.
Health & Wellness (1 Credit Unit)
This is a Level 1 Core module for all Year 1 students. The module will introduce students to the importance of maintaining both physical and mental health through the knowledge and monitoring of health indicators, and application through appropriate exercises. The aim of the module is to empower students with basic knowledge and skills to be independent and responsible in maintaining overall personal health.
Innovation Made Possible^ (3 Credit Units)
^ Critical Core modules account for 10 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in innovation and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
Databases (4 Credit Units)
Today’s business organisations depend on information systems in virtually all aspects of their businesses. Corporate databases are set up to hold the voluminous business transactions generated by these information systems. This module introduces students to the underlying concepts of database systems and how to model and design database systems that reflect business requirements. Students will be taught how to analyse data needs, model the relationships amongst the data entities, apply the normalisation process to relations and create the physical database. Skills taught include data modelling technique, transformation of data model to relations, normalisation technique and SQL (Structured Query Language).
Data Discovery & Visualisation (4 Credit Units)
This module discusses the principles and techniques for creating effective visualisations based on graphic design and perceptual psychology. Using widely adopted tools, learners will apply these principles and techniques to create rich visualisations for analysis and presentation. Indicative topics include Principles of Visualization, Dashboard Design Techniques and Designing for an Audience.
Mathematics for Data Science (4 Credit Units)
In this module, students will first be exposed to statistical concepts, including hypothesis testing, probability distribution and more. Students will be able to perform univariate, multivariate and correlation analysis in order to identify inherent patterns and derive key insights from business data. Indicative topics include Normal Distribution, Sampling and Sampling Distributions and Correlation Analysis.
Programming 2 (4 Credit Units)
This module builds upon the knowledge and skills acquired in Programming I. It aims to provide opportunities for the students to develop medium-scale applications based on the Object-Oriented (OO) approach. A suitable object- oriented high-level programming language will be used by students to apply in their problem-solving skills. The main concepts of OO and the implementation of applications using the OO approach will be taught in this module.
The module may cover the concepts of Abstract Data Types (ADTs) and the implementation of some selected ADTs using the OO approach. Suitable sorting and search algorithms and the use of Application Protocol Interface (API) will be introduced when required. Other key topics include the introduction of system design concepts such as the class diagram. Software robustness and correctness, and good programming practices will be emphasised throughout the module. Independent and self-directed learning will also be encouraged.
Confident Communication: Find Your Voice (VOICE)^ (3 Credit Units)
^ Critical Core modules account for 10 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in innovation and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
Intelligent Enterprise Systems (4 Credit Units)
The use of intelligent enterprise systems has become a necessity in multi-national companies as well as small and medium enterprises. This module introduces students to the different components that build up an intelligent enterprise system. Students
will be able to appreciate the complexity of business processes, how IT can help organisations to be more competitive and gain basic management skills that are required to manage business processes in an organisation.
Machine Learning I (4 Credit Units)
This module provides a comprehensive introduction to Machine Learning and its practical applications. Students will acquire the necessary foundational knowledge and context to understand Machine Learning. They will explore various supervised and unsupervised learning models, including Linear and Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, K-means Clustering, and more. By following an experiential learning approach, students will actively engage in implementing and training basic Machine Learning models using relevant coding libraries.
Data Wrangling (4 Credit Units)
This module focuses on the use programming libraries and shell scripting techniques to clean and prepare data for analysis and modelling purposes. Emphasis will be placed on the Extraction, Transformation, and Loading (ETL) of data sets. Indicative topics
include Storage and Database Connections, Manipulation of Datasets and Web Scraping.
Fundamentals for IT Professionals 2 (2 Credit Units)
This module gives a course-based experience in which students can engage with the local community and industry. This includes participation in community service events or in Service-Learning projects that leverages on students’ discipline knowledge
and skills to meet identified needs. Through iterative and guided reflection on the service experience, students gain a broader appreciation of their discipline and an enhanced sense of personal voice, empathy and civic responsibility. Industry talks
and seminars are organised to keep students up to-date with emerging trends and develop their interpersonal, team and networking skills with the community and industry.
Elective Module 1# (4 Credit Units)
World Issues: A Singapore Perspective^ (2 Credit Units)
^ Critical Core modules account for 10 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in innovation and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
Agile DataOps (4 Credit Units)
This module explores the end-to-end cycle of data analytics through a DataOps framework. Students will be introduced to the motivations behind DataOps such as the Agile framework, how DataOps can add significant value to analytics development and deployment,
and also the best practices in DataOps. Indicative topics include Agile Data Warehousing, Innovation for DataOps and Test Automation.
Machine Learning II (4 Credit Units)
This module allows students to use leading software and associated libraries, to develop more sophisticated supervised learning and unsupervised learning models to solve real-life problems. Students will acquire a comprehensive understanding of Machine Learning and gain exposure to more complex Machine Learning model algorithms such as Ensemble modelling. Using leading software and associated libraries, students will be able to implement and train Machine Learning models to address business challenges.
Emerging Trends in Data Science (2 Credit Units)
This module explores the latest trends and technologies in the areas of Data Science, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics. Students will be exposed to fresh developments and prominent discoveries in machine learning techniques, growth in the areas of AI solutions, as well as ethical issues and governance pertaining to the use of AI solutions and Data Science applications.
Fundamentals for IT Professionals 3 (2 Credit Units)
This module provides a stepping stone to the students in their IT career. Students are given an insight into the infocomm industries and are kept abreast of the updates and the necessary skill sets required in their IT career path. They also have the
opportunity to be exposed to the various institutes of higher learning to further enhance their skill sets.
Elective Module 2# (4 Credit Units)
Elective Module 3# (4 Credit Units)
Capstone Project (8 Credit Units)
In this module, students are required to complete a substantial project that is the culmination of their education in the School of InfoComm Technology. The project can be a real-world problem proposed by a client, or it can be proposed by the student in pursuit of their personal interests.
Internship II
This module provides students with the opportunity to apply the knowledge and skills gained from the various modules in the course to the development of an IT solution to solve a practical problem. Students may undertake a real-life IT project in an organisation that may include problem definition, requirements analysis, design , development and testing, delivery and presentation of the solution. Through the project, students will learn and appreciate the project planning and control issues relating to IT project development.
Elective Module 4# (4 Credit Units)
Elective Module 5# (4 Credit Units)
Elective Module 6# (4 Credit Units)
Elective Module 7# (4 Credit Units)
Project ID: Connecting the Dots ^ (4 Credit Units)
^ Critical Core modules account for 10 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in innovation and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
Internship/Project (20 Credit Units)
This module provides students with the opportunity to apply the knowledge and skills gained from the various modules in the course to the development of an IT solution to solve a practical problem. Students may undertake a real-life IT project in an organisation that may include problem definition, requirements analysis, design, development and testing, delivery and presentation of the solution. Through the project, students will learn and appreciate the project planning and control issues relating to IT project development.
Specialisation: Generative AI
Deep Learning (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces the fundamentals of Deep Learning and its applications. Students will be provided essential context and background knowledge around Artificial Intelligence and its subset, Deep Learning. Students will learn about deep learning models
such as Neural Networks and experience the practical applications of these models in areas such as computer vision and natural language processing. Students will implement deep learning models using leading software and associated libraries. Various
types of deep learning models will be implemented, and students will be taught to train the models and improve their performance.
Generative AI Tools & Techniques (4 Credit Units)
In this module, students will learn to craft efficient prompts for AI systems using indicative techniques such as Prompt Engineering and LangChain. Students will learn the necessary procedures to fine-tune Large Language Models (LLMs), encompassing
tasks such as data preparation, training, and evaluating fine-tuned models, empowering students to fine-tune LLMs to align with the specific requirements of their organisations. This module also serves as an introduction to the utilisation
of diffusion models for image generation applications. Furthermore, students will learn to design and create useful applications.
Generative AI Solutioning (4 Credit Units)
This module will cover the fundamental principles of Generative AI in text and image generation. The basics of visual generative models, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) for creating images, videos, and their various applications, will
be introduced. In the context of Generative AI in natural language processing, the fundamentals of sequential generative models used to create or generate new text content will be covered. There will be opportunities for students to experience
the practical applications of these models. Emphasising hands-on experiential learning, students will actively code and implement these generative AI models for text and image generation tasks using relevant libraries.
Specialisation: Data Engineering
Distributed Data Pipelines (DDP) (4 Credit Units)
This module will introduce various aspects of data engineering concepts through the building of resilient distributed databases, such as Hadoop and Spark platforms. Students will understand how to extract valuable data from multiple sources and propose
scalable solutions where appropriate. Indicative topics include Tools and Platforms for Big Data, Structures and Schemas for Big Data and Streaming Tools and Platforms.
Data Virtualisation (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces the fundamentals of data virtualisation, where students will explore techniques to leverage data virtualisation as a critical tool in the data ecosystem. Students will learn to harness the power of data virtualisation
to streamline data management, accelerate decision-making, and enhance data driven insights. Through hands-on exercises, students will be able to apply the basic techniques of creating virtual data layers, optimising data access, and ensuring
data consistency, all while reducing the complexities of traditional data integration.
Data Lake and Data Warehouse (4 Credit Units)
This module equips students with the essential understanding and knowledge of Data Lakes and Data Warehouses, enabling them to effectively leverage these storage repositories to address various business requirements. Students will learn the fundamental
differences between Data Lakes and Data Warehouses as well as their respective strengths and weaknesses. Indicative topics include data modelling, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, and data governance strategies tailored to storage & repositories.
General Track
Capstone Project (8 Credit Units)
In this module, students are required to complete a substantial project that is the culmination of their education in the School of InfoComm
Technology. The project can be a real-world problem proposed by a client, or it can be proposed by the student in pursuit of their personal interests.
Internship II (16 Credit Units)
This module provides students with the opportunity to apply the knowledge and skills gained from the various modules in the course to the development of an IT solution to solve a practical problem. Students may undertake a real-life IT project in an organisation
that may include problem definition, requirements analysis, design, development and testing, delivery and presentation of the solution. Through the project, students will learn and appreciate the project planning and control issues relating to IT
project development.
AI Tools & Techniques for Cybersecurity (4 Credit Units)
This module trains students on various cybersecurity-related AI tools & techniques used by the industry. Students will learn how to setup, configure, train, execute, operate, and manage these AI tools & techniques to harden
security, detect cyberattacks, respond to cyber incidents, and restore normal operations.
Artificial Intelligence Concepts and Techniques (4 Credit Units)
This module covers the fundamental concepts and techniques of artificial intelligence (AI). Students will learn basic knowledge representation, how machines can engage in problem solving, reasoning and learning with computational
perspective. Indicative topics include reasoning, search, constraints, planning and game playing, learning. Students will gain an understanding of the AI algorithms and apply them to develop intelligent systems to solve problems.
Blockchain (4 Credit Units)
This module will introduce students to block-chain concepts and how these are being applied using industry use cases. Students will also have hands on experience to create transactions on a
block-chain to better understand the underlying concepts. Students will get a chance to develop to build their own Smart Contracts to be executed on the block-chain.
Cloud Databases (4 Credit Units)
This module builds upon the knowledge and skills acquired in the Databases module. It covers the analysis, design, and implementation of cloud database models to support polyglot-persistence architecture for modern software applications, and data management life cycle. Latest cloud storage models and techniques (such as document and graph databases), and various database systems (such as NoSQL database, parallel and distributed databases) are introduced.
In addition, students are exposed to denormalisation and data partitioning strategies for designing and implementing such systems. The module also provides an insight into migrating data onto cloud databases.
Cloud Architecture and Technologies (4 Credit Units)
This module gives insight into the key concepts and technologies of cloud computing, which include cloud characteristics, service models (SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS), deployment models (Public cloud, Private cloud, Community cloud, and Hybrid cloud), and the features of cloud computing technologies. It also covers the cloud computing architecture, emerging trends, and issues such as clouds for mobile applications, cloud portability and interoperability, scalability, manageability, and service delivery in terms of design and implementation issues. The module discusses the benefits and challenges of cloud computing, standards of cloud computing service delivery, and Service Level Agreements
(SLAs) for cloud services. Hands-on activities are included to expose students to various cloud computing services offered by major cloud computing providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google App Engine (GAE), and Microsoft Windows Azure.
Customer Experience Management (4 Credit Units)
With SMAC (Social, Mobility, Analytics and Cloud) technologies resulting in a new competitive environment, the control has shifted from the seller to buyer. This module provides students with the knowledge and understanding of Customer Experience Management (CXM) as a business strategy in this new environment. The buyer's experience is not limited to a single transaction but includes the sum of all experiences across all touch points and channels between
a buyer and a seller over the duration of their relationship. This strategy aims to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage to help sellers manage the buyer's experience that is both collaborative and personalised.
Students will have an opportunity to have hands-on experience with customer management systems used by sellers that collect and create customer data, segment that data into manageable data sets, make sense of the data and make it available for timely delivery. This allows companies to deliver consistent customer experiences that delight customers or achieve other organisational goals
Designing User Experience (4 Credit Units)
This module aims to equip students with skills and techniques to fulfil the various stages of the UX design process, leading to optimum user-centric digital products. Exposure to various problem statements will aid students in developing
critical, analytical perspectives for framing their approaches to problem-solving. Other major topics include: Research methods, Interaction Design, Rapid Prototyping, Measuring User Experience and Usability Testing. Students are also guided on how to compile a proper UX portfolio.
Digital Transformation (4 Credit Units)
This module will discuss how digital disruption and technologies continue to drastically alter competitive dynamics across industry and businesses. Using digital transformation framework, students will learn how to assess an organisation by looking at their people, culture, leadership, processes, technology, and data, and to develop digital transformation strategy that is tied to the business outcomes and goals.
Emerging AI Trends in Cybersecurity (4 Credit Units)
This module is designed to help students keep abreast of the latest AI developments in cybersecurity, to stay current and relevant in the fast-moving industry. To achieve this objective, the syllabus for this module will be guided
by AI research and feedback from industry partners, and both seminar-style and hands-on workshop teaching approaches may be adopted depending on the nature of the topic covered
Financial Ecosystem (4 Credit Units)
This module provides a macro-overview of the network of organisations involved in the delivery of financial services through both competition and cooperation. Students will be introduced to the various participants in the financial
ecosystem, which includes financial intermediaries, regulators, market operators, industry associations and customers. Subsequently, students would also learn about the market microstructures, interactions and interdependencies underlying
the relationships intertwining these participants. Additionally, students would learn about the ongoing digital evolution in the financial sector and its future implications for all participants.
Infocomm Sales & Marketing Strategies (4 Credit Units)
This module will introduce students to the concept of market segmentation and the development of sales and marketing strategies for each segment. They will acquire
an understanding of industry and customer segmentation from corporate, small and medium businesses to consumers. They will also delve into the different go-to-market strategies and selling techniques required in the context of ICT (such as consultative
selling, major account selling and management, territory selling and management, partner management and consumer marketing).
Machine & Deep Learning Applications for Cybersecurity (4 Credit Units)
This module teaches students machine learning and deep learning algorithms and their applications for cybersecurity. Students will learn how to effectively use machine learning and deep learning to detect and mitigate various cyber threats and attacks.
Mobile Applications Development (4 Credit Units)
This module builds upon the programming skills and knowledge that students have acquired from the course to date, to develop software solutions on mobile platforms. It
will explore the recent developments in mobile technologies and operating systems and focus on the development of applications on these emerging mobile operating systems. The module presents the techniques for mobile app development, covering mobile
app architecture as well as key factors to consider, to develop effective accessible mobile software solutions. The students will have the opportunity to apply their knowledge and skills in practice to develop mobile applications in domain areas of
their interest, such as entertainment, games, and healthcare.
Modern Artificial Intelligence (4 Credit Units)
This module provides students with an introduction to artificial intelligence (AI) and an overview of how AI can be applied in industries and real-world problems in the modern world today. The module will discuss and analyse existing
and possible future implementations of AI solutions across various industries and explore opportunities available for AI application when considering human interaction with digital systems. The students may also learn
the major building blocks and terminology in AI technology. At the end of the course, students will learn how to propose high-level solutions to different problems and industries using AI.
Reinforcement Learning (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces the field of Reinforcement Learning (RL), which is useful in creating automated systems that learn to make decisions. It will first cover key features of RL, followed by its fundamental approaches and algorithms.
Indicative topics may include Policy Iteration, Markov Decision Processes, Monte Carlo Methods, Temporal-Difference (TD) Learning, Q-Learning, Value Function Approximation. The students will then apply the concepts and techniques
learnt to solving real-world problems.
- Economics
- Finance & Accounting for Business
- Financial Markets & Instruments
- Global Business
- Business Law
- Corporate Finance
- Develop a Business
- People & Culture
- Marketing in the Digital Age
Video Showcase
DS in 60 Seconds
NP to roll out specialisation in generative AI next year
29 Dec 2023 | Lianhe Zaobao
Synopsis: NP is partnering with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to co-develop a specialisation in generative AI. Students in NP’s Data Science course will be able to specialise in either Data Engineering or Generative AI in their second year and get a chance to embark on a one-year internship with AWS. NP and AWS also plan to launch a centre in campus for training and consultancy services. Deputy Principal Mah Wee Beng shared that the course is expected to admit 50 students next year. Other polytechnics are also rolling out similar courses that cover AI and data analytics.
8 Jan 2024 | The Straits Times (Online, Print)






